Cervical Insufficiency: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Pregnancy Management
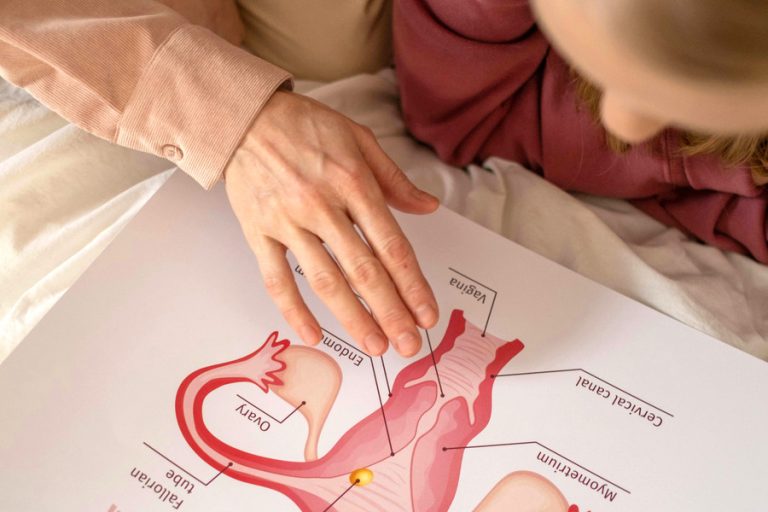
Cervical insufficiency, sometimes called an incompetent cervix, is a condition in which the cervix shortens, softens, or opens too early during pregnancy – often without pain or contractions. This can lead to pregnancy loss or preterm birth, usually in the second trimester.
While the diagnosis can feel overwhelming, early detection and proper care can significantly improve pregnancy outcomes.
What Is Cervical Insufficiency?
Cervical insufficiency occurs when the cervix is unable to stay closed and firm throughout pregnancy. Normally, the cervix remains tightly closed until late pregnancy or labor. In cervical insufficiency, the cervix begins to open prematurely under the weight of the growing pregnancy.
This condition is not caused by labor contractions and often develops silently.
How Common Is Cervical Insufficiency?
Cervical insufficiency affects about 1% of pregnancies, but it is more common among women with a history of second-trimester pregnancy loss or preterm birth.
Causes of Cervical Insufficiency
In many cases, the exact cause is unknown. However, several factors increase the risk:
1. Previous Cervical Trauma
Prior dilation and curettage (D&C)
Cervical surgery (such as LEEP or cone biopsy)
Injury during a previous childbirth
2. Congenital Cervical or Uterine Conditions
Naturally weak or short cervix
Uterine malformations
3. Connective Tissue Disorders
Conditions like Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
4. Multiple Pregnancies
Carrying twins or more increases pressure on the cervix
Signs and Symptoms
Cervical insufficiency often presents with few or no warning signs. When symptoms do occur, they may include:
Pelvic pressure
Lower back pain
Mild abdominal cramping
Increased vaginal discharge
Light spotting or bleeding
Because symptoms can be subtle, routine prenatal care is essential.
How Is Cervical Insufficiency Diagnosed?
Diagnosis is based on medical history and imaging.
1. Medical History
A history of painless cervical dilation, second-trimester losses, or preterm births raises suspicion.
2. Transvaginal Ultrasound
Measures cervical length. A cervix shorter than 25 mm before 24 weeks may indicate insufficiency.
3. Physical Examination
In some cases, early cervical dilation may be detected during a pelvic exam.
Treatment and Management Options
Management depends on gestational age, symptoms, and pregnancy history.
1. Cervical Cerclage
A surgical procedure in which stitches are placed around the cervix to keep it closed.
Types include:
Prophylactic cerclage (placed early in pregnancy)
Ultrasound-indicated cerclage
Emergency or rescue cerclage
Cerclage has been shown to reduce the risk of preterm birth in appropriate cases.
2. Progesterone Therapy
Progesterone may be given vaginally or via injection to help maintain pregnancy and reduce preterm birth risk.
3. Activity Modification
In some cases, reduced physical activity or pelvic rest may be advised.
4. Close Monitoring
Frequent ultrasounds and prenatal visits help track cervical length and pregnancy progress.
Pregnancy Outcomes With Cervical Insufficiency
With early diagnosis and proper management:
Many women carry pregnancies to term or near-term
Risk of pregnancy loss is significantly reduced
Healthy delivery outcomes are achievable
Can Cervical Insufficiency Be Prevented?
While it cannot always be prevented, risk reduction includes:
Early prenatal care
Cervical length screening for high-risk women
Timely intervention when changes are detected
When to Contact a Healthcare Provider
Seek immediate medical care if you experience:
Pelvic pressure or a feeling that something is “coming down”
Sudden increase in vaginal discharge
Vaginal bleeding
Lower back pain during pregnancy
Prompt evaluation can be life-saving for the pregnancy.
Emotional Impact and Support
Experiencing cervical insufficiency can be emotionally challenging, especially for women with previous pregnancy loss. Emotional support, counseling, and open communication with healthcare providers are important aspects of care.
Final Thoughts
Cervical insufficiency is a serious but manageable condition. With awareness, early diagnosis, and appropriate treatment, many women go on to have successful pregnancies. If you have risk factors or concerns, proactive care and regular prenatal visits are essential.
Knowledge empowers expectant mothers to advocate for their health and seek timely support.