Birth Control: Everything You Need to Know About Contraceptive Options
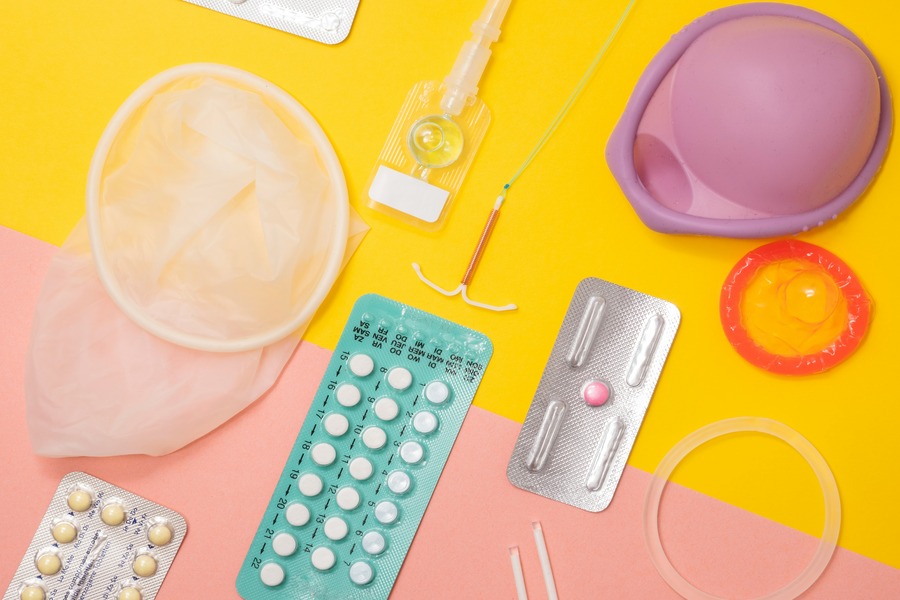
Birth control includes any method, medication, device, or procedure used to prevent pregnancy. Some methods are also used to treat health issues like acne, heavy periods, endometriosis, or hormonal imbalances.
There are five main categories of birth control:
Hormonal Methods
Barrier Methods
Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
Permanent Methods
Behavioral or Natural Methods
1. Hormonal Birth Control Methods
These methods use synthetic hormones (estrogen, progestin, or both) to prevent ovulation, thicken cervical mucus, or thin the uterine lining.
a. Birth Control Pills
Taken daily
Types: Combined pill (estrogen + progestin) or progestin-only
Pros: Regulates periods, reduces acne, may lower risk of some cancers
Cons: Must be taken daily; may cause nausea, mood changes
b. Birth Control Patch
Worn on the skin and changed weekly
Releases estrogen and progestin
Pros: Easy to use, effective
Cons: Can cause skin irritation; slightly higher risk of blood clots
c. Birth Control Ring (NuvaRing)
A flexible ring inserted into the vagina monthly
Releases hormones locally
Pros: Once-a-month use
Cons: May cause vaginal irritation
d. Birth Control Shot (Depo-Provera)
Injection every 3 months
Contains progestin only
Pros: Very effective; doesn’t require daily action
Cons: May cause weight gain, delayed return to fertility
e. Hormonal Implants (Nexplanon)
A small rod placed under the skin of the arm
Effective for up to 3 years
Pros: Low maintenance, highly effective
Cons: May cause irregular bleeding initially
2. Barrier Methods
These physically prevent sperm from reaching the egg.
a. Male Condoms
Worn on the penis during sex
Pros: Protects against STIs; no prescription needed
Cons: May break or slip
b. Female Condoms
Worn inside the vagina
Pros: STI protection; can be inserted ahead of time
Cons: Less common, harder to find
c. Diaphragms and Cervical Caps
Dome-shaped devices inserted into the vagina to cover the cervix
Used with spermicide
Pros: Reusable
Cons: Less effective than other methods; must be fitted by a doctor
d. Spermicide
A chemical that kills sperm, available as gels, foams, films
Often used with other barrier methods
Cons: Can cause irritation or allergic reactions
3. Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
Small, T-shaped devices inserted into the uterus by a healthcare provider.
a. Hormonal IUDs (Mirena, Kyleena, Liletta, Skyla)
Release progestin
Last 3–8 years depending on type
Pros: Highly effective, can lighten or stop periods
Cons: May cause cramping initially
b. Copper IUD (Paragard)
Non-hormonal; releases copper to prevent sperm movement
Lasts up to 10 years
Pros: Hormone-free
Cons: May cause heavier periods and cramping
4. Permanent Birth Control Methods
For individuals who are certain they do not want children in the future.
a. Tubal Ligation (Female Sterilization)
Surgical procedure to block or cut fallopian tubes
Pros: Permanent
Cons: Requires surgery; not easily reversible
b. Vasectomy (Male Sterilization)
Cuts or seals the vas deferens (sperm-carrying tubes)
Pros: Safe, effective, and permanent
Cons: Takes a few months to become fully effective; requires follow-up
5. Behavioral and Natural Methods
These rely on timing, tracking, and abstinence during fertile days.
a. Fertility Awareness (Natural Family Planning)
Tracking ovulation signs (temperature, cervical mucus)
Pros: No side effects; accepted in religious contexts
Cons: Requires daily tracking and discipline; less reliable
b. Withdrawal Method
Pulling out before ejaculation
Pros: No cost
Cons: High failure rate; pre-ejaculate may contain sperm
c. Abstinence
Avoiding sexual activity
Pros: 100% effective if practiced consistently
Cons: Requires commitment; not always realistic long-term
Emergency Contraception
Used to prevent pregnancy after unprotected sex or contraceptive failure.
a. Morning-After Pill (Plan B, Ella)
Most effective when taken within 72–120 hours
Pros: Available over the counter (in most places)
Cons: May cause temporary side effects like nausea or cycle changes
b. Copper IUD as Emergency Contraception
Can be inserted up to 5 days after unprotected sex
Most effective emergency method
How to Choose the Right Birth Control
Consider the following factors:
Effectiveness: What’s your risk tolerance for unintended pregnancy?
Lifestyle: Do you prefer daily, monthly, or long-term methods?
Medical history: Any hormonal sensitivities or health conditions?
Family planning goals: Do you want kids now, later, or not at all?
STI protection: Only condoms provide STI protection
Cost and accessibility: Some methods require prescriptions or insurance coverage
A conversation with your healthcare provider can help guide the best decision for your needs and preferences.
Benefits of Birth Control Beyond Pregnancy Prevention
Regulates menstrual cycles
Reduces menstrual cramps and PMS
Improves acne
Manages endometriosis or PCOS
Lowers risk of certain cancers (like ovarian and endometrial)
Common Side Effects and Risks
Nausea, breast tenderness, mood changes
Spotting between periods
Headaches
Increased risk of blood clots (in some hormonal methods)
Insertion pain or adjustment period for IUDs and implants
Most side effects are temporary and manageable, but always consult your provider if symptoms persist.
Final Thoughts
Birth control is a deeply personal decision, and no single method is right for everyone. The key is to stay informed, weigh your options, and revisit your needs regularly—because what works for you now might change over time.
Whether you’re preventing pregnancy, managing a health condition, or simply planning for the future, there’s a method that can support your goals.
Your body, your choice, your control. Take the time to choose what’s best for you.