Understanding Women’s Fertility: A Guide to Reproductive Health
Fertility is an important aspect of women’s health, closely tied to the ability to conceive and carry a pregnancy. For many women, understanding fertility helps with family planning, identifying health concerns, and making informed decisions about reproductive care.
What Is Fertility?
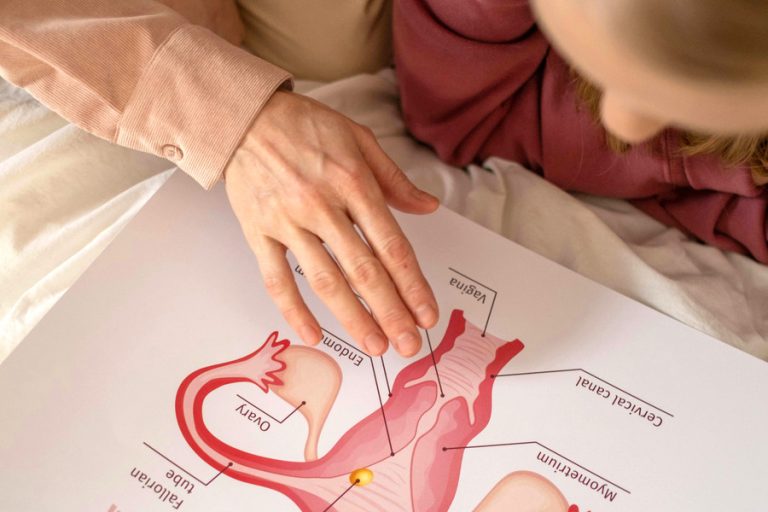
Fertility refers to a woman’s natural ability to conceive a child. It depends on several factors, including the health of the reproductive organs, hormone levels, ovulation, and overall well-being.
While fertility varies among individuals, age, lifestyle, and medical conditions all play important roles.
How Women’s Fertility Works
Fertility is primarily regulated by the menstrual cycle, which prepares the body for potential pregnancy each month.
Ovulation: Around the middle of the cycle, one of the ovaries releases an egg.
Fertilization: If sperm reaches and fertilizes the egg, conception occurs.
Implantation: The fertilized egg implants into the uterine lining, where pregnancy begins.
Menstruation: If no fertilization occurs, the uterine lining sheds, resulting in a period.
The fertile window—the few days before and during ovulation—is when pregnancy is most likely to occur.
Factors That Influence Fertility
Several elements can affect a woman’s ability to conceive:
1. Age
Fertility peaks in the late teens to late 20s.
After age 35, fertility declines more significantly due to reduced egg quantity and quality.
2. Hormonal Health
Hormones regulate ovulation and the menstrual cycle. Imbalances can disrupt fertility.
3. Reproductive Health Conditions
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Endometriosis
Uterine fibroids
Blocked fallopian tubes
4. Lifestyle Factors
Smoking, excessive alcohol, and drug use lower fertility.
Poor diet, obesity, or being underweight can disrupt ovulation.
High stress levels may affect hormonal balance.
5. General Health
Chronic conditions like diabetes or thyroid disorders can influence reproductive function.
Signs of Fertility Issues
It may be time to seek medical advice if you experience:
Irregular or absent menstrual cycles
Painful periods or intercourse
Difficulty conceiving after 12 months (or 6 months if over 35)
History of pelvic infections or reproductive disorders
Fertility Testing and Diagnosis
Doctors may recommend tests such as:
Hormone blood tests to check ovarian reserve and hormone balance.
Ultrasound scans to examine the uterus and ovaries.
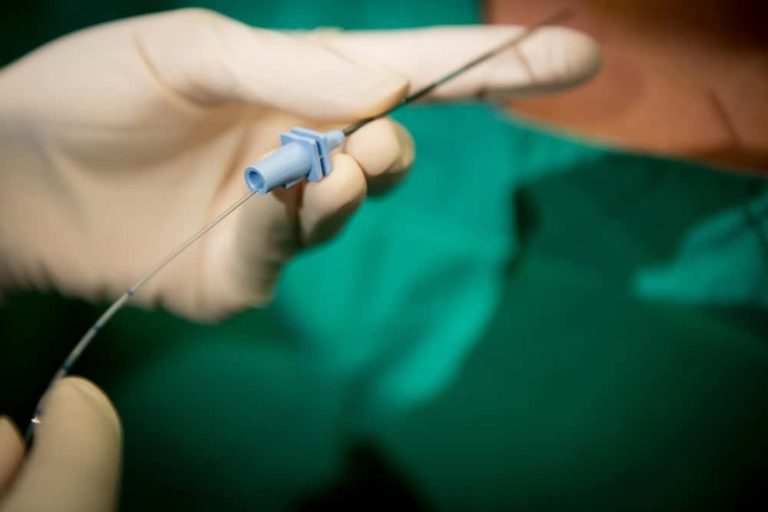
Hysterosalpingography (HSG) to check if fallopian tubes are open.
Partner evaluation to assess sperm health, since fertility involves both partners.
Treatment Options for Fertility Problems
Depending on the cause, treatment may include:
Medications to stimulate ovulation or balance hormones.
Surgery to remove fibroids, cysts, or scar tissue.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART):
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): Placing sperm directly into the uterus.
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): Fertilizing eggs outside the body and transferring embryos to the uterus.
Lifestyle changes to improve overall reproductive health.
Tips to Support Fertility Naturally
Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
Maintain a healthy weight.
Exercise regularly but avoid excessive intense workouts.
Limit alcohol and caffeine, and avoid smoking.
Track menstrual cycles to understand ovulation patterns.
Manage stress through relaxation techniques, yoga, or mindfulness.
Final Thoughts
Women’s fertility is influenced by many factors, from age and hormones to lifestyle and medical conditions. While some challenges may arise, advances in reproductive medicine offer many options for women and couples hoping to conceive.
Understanding your fertility, practicing healthy habits, and seeking timely medical advice can empower you to make informed choices for your reproductive health and future.